Sunday 22 February 1942
 |
| A local St. Louis girl, Nurse Agnes Kozjak, in her field uniform at Ft. Benning, Georgia. St. Louis Post-Dispatch, Pictures Section, page 1, February 22, 1942. |
Battle of the Pacific: The loss of the Allied position on the Bilin River and the resulting approach of Japanese troops causes panic in Rangoon on 22 February 1942. Civilians evacuate west to India or leave by sea. On the Sittang River, the last strong natural barrier between the Japanese Army and Rangoon, the Japanese continue to make gains. Throughout the day, the British Indian Army continues to hold the Sittang River Bridge despite fierce Japanese attacks, often at close quarters. Finally, at 17:30, Brigadier Sir John George Smyth, V.C., orders his troops to blow up the bridge rather than allow it to fall into Japanese hands intact. This is done despite the fact that a large portion of the 17th Indian Division is still on the other side. Those men now are forced to get across the river in small groups without their equipment, and most of them do manage to reach the British lines. The overall commander in Burma, General Hutton, soon dismisses Smyth and replaces him as commander of the 17th Division with Brigadier David "Punch" Cowan. Since the 17th Division is the only large force available to defend the Sittang River, its struggles now for all intents and purposes doom Rangoon.
US Navy submarine USS Swordfish disembarks Philippine President Manuel Quezon and his party at San Jose, Panay. Quezon wants to set up a new headquarters in Mindanao, but the Allies want him out of the Philippines and in Australia. They fear that Quezon may make a separate peace with the Japanese, which would remove from battle many troops fighting hard in the Bataan Peninsula. Area commander General Douglas MacArthur, meanwhile, also has orders to leave the Philippines and head to Australia.
After dark, two flights of 3 B-17Es of the Kangaroo Squadron (435th Bomb Squadron of the 19th Bomb Group), six bombers in all, set out from Townsville (Queensland) Field to bomb the Japanese fortress at Rabaul. The raid will actually take place early on the morning of the 23rd. One of these B-17s is "Swamp Ghost," which later becomes famous for being found in the swamps of New Guinea. The area has become too hot now for the US Navy to realize its plans of sending a carrier task force to attack the port, which rapidly is becoming the main Japanese base in the southwest Pacific.
European Air Operations: After dark, RAF Bomber Command sends 50 bombers (31 Wellingtons and 19 Hampdens) to attack Wilhelmshaven. The targets are German heavy cruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau ("Salmon and Gluckstein" as the British call them, after the tobacconist), which are believed to be at anchor. The weather is poor for bombing and bombers attempt to release their loads over the city instead (and, according to the Germans, they all miss Wilhelmshaven entirely). Seven bombers attack Emden, five bombers bomb the port of Ostend, five Manchesters lay mines off of Wilhelmshaven, and two Hampdens drop leaflets over Paris. The RAF loses no aircraft.
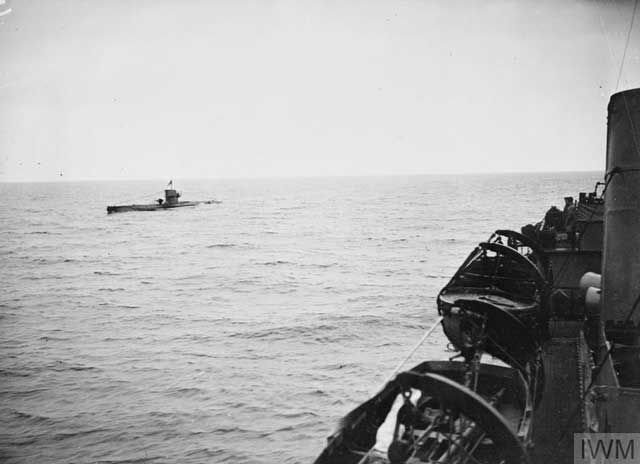
Battle of the Atlantic: U-504 (KrvKpt. Hans-Georg Friedrich Poske), on its second patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes and sinks 5287-ton US freighter Republic about 3 1/2 miles (5 km) northeast of Jupiter Inlet, Florida. While the Republic remains afloat for over 24 hours, it drifts onto reefs about five miles east of Hobe Sound and is lost. This is one of the famous incidents near Florida in which residents onshore are able to see the attack or its result. The surviving crewmen row ashore and are helped by local citizens. There are five dead and 29 survivors.
U-96 (Kptlt. Heinrich Lehmann-Willenbrock), on its third patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes and sinks 6,999-ton British freighter Scottish Standard, a straggler from Convoy ONS-67 The crew of Scottish Standard already has abandoned the ship after bombing by a German Focke-Wulf Fw200 Condor, but Lehmann-Willenbrock gladly administers the coup de grâce at 15:52. There are five dead and 39 survivors.
U-96 also hits 8888-ton British tanker Kars, another straggler, this one from Convoy HX-175 (convoys often overlap on the busy North Atlantic routes). The ship is abandoned and taken in tow. Kars makes it to Halifax and is beached on 27 February. There are 50 deaths and two survivors.
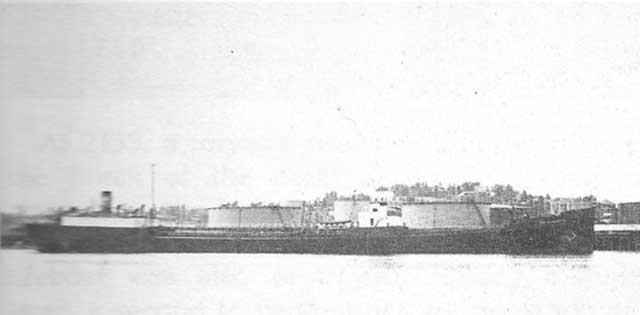
U-155 (Kptlt. Adolf Cornelius Piening), on its first patrol out of Kiel, gets its first two victories of the war. They are 1799-ton Norwegian freighter Sama and 7984-ton British freighter Adellen. Both of these ships are part of Convoy ONS-67. Both ships are hit after U-155 firest three torpedoes into the convoy south of Cape Farewell. There are 36 dead and 12 survivors from the Adellen and 19 dead and 20 survivors from Sama.
U-128 (Kptlt. Ulrich Heyse), on its second patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes and sinks unescorted 8103-ton US tanker Cities Service Empire about 25 miles north of Bethel Shoals, Florida. Heyse fires four torpedoes at the ship but misses with all four. He then fires two more torpedoes. These hit and immediately start a raging fire. There are 14 dead and 36 survivors.
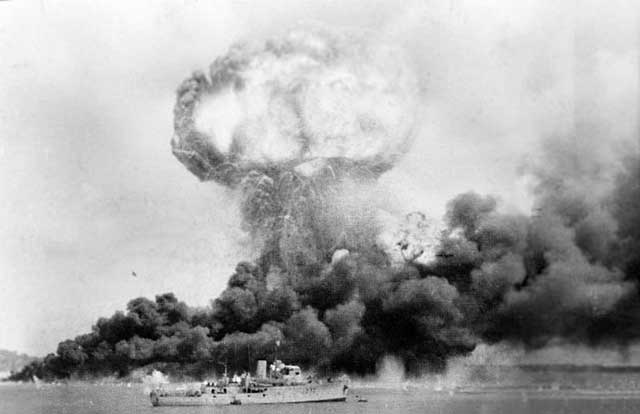
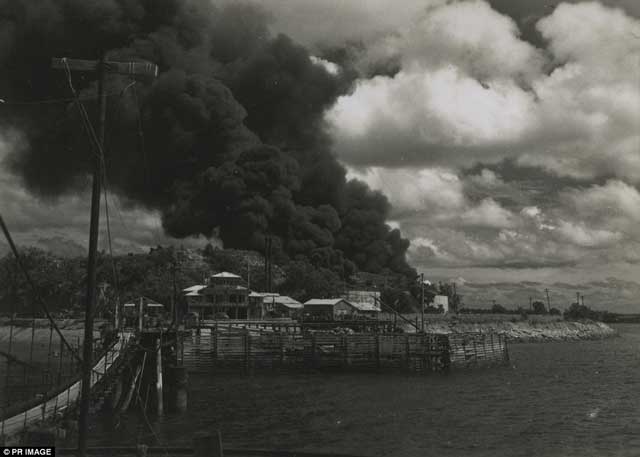
Battle of the Mediterranean: The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks British 1341-ton freighter Hanne (formerly City of Bradford) in the Mediterranean about 77 miles east of Tobruk. The Hanne was carrying military equipment, something it had done 21 times already without incident. There are four deaths and 21 survivors.
U-83 (Kptlt. Hans-Werner Kraus), on its fifth patrol out of Salamis, claims to hit two ships near Sidi Barrani with torpedoes. This may be true, but there are no records of damaged ships at this time and place.
German Resistance: Ernst Junger, who maintains a personal diary, has tea with General of Infantry Carl-Heinrich Rudolf Wilhelm von Stülpnagel, who is the new military commander of Occupied France (succeeding his cousin, General Otto von Stülpnagel). Junger, who is on Stülpnagel's staff, finds that Stülpnagel is unexpectedly pessimistic about the military situation on the Eastern Front (where Stülpnagel commanded the 17th Army). Stülpnagel also complains about a hidden battle in France for power between the military occupation authority and the NSDAP. The former is acting in furtherance of military goals while the latter is more interested in political control. Stülpnagel is maintaining contacts with the anti-Hitler resistance through his friend, Lieutenant-Colonel Caesar von Hofacker. However, Stülpnagel is no angel and is alleged to authorize war crimes in his commands.
Holocaust: German Einsatzgruppe C sets up the Dzyatlava Ghetto (Zdzięcioł Ghetto) in Western Belarus when troops plaster city walls with posters directing the 4500 Jewish residents to relocate to an area around the synagogue and the Talmud Torah building within the streets of Łysogórska and Słonimska. Other residents are forced to evacuate their homes (which they gladly do so as to not be in the Ghetto themselves) and they are used for the new arrivals. The Ghetto is at least partially surrounded by barriers and barbed wire, with guards controlling access. Some trade is permitted between residents of the Ghetto and people outside for things like food and clothing, but these interactions are extremely limited. The Ghetto residents are used for building tasks outside the Ghetto under close guard.
British Military: Air Marshall Arthur Harris becomes Head of Bomber Command for the RAF. He becomes known as "Bomber" Harris for his enthusiastic implementation of the RAF's new policy of terror bombings (the Area Bombing Directive of 14 February 1942).
Harris puts forth his views on the upcoming bombing campaign by reference to the Bible:
US Military: Recently arrived Major General Ira C. Eaker sets up the headquarter of U.S. Army Bomber Command, U.S. Army Forces, British Isles (USAFBI).
US Navy seaplane tender USS Langley leads a convoy of ships out of Freemantle, Australia, to India and Tjilatjap, Java. They carry 69 USAAF P-40s, motor vehicles, and U.S. Army troops
The A-24s of the 17th Bombardment Squadron, 27th Bomber Group, arrive at Batchelor from Brisbane, Australia. As with many air units in the region, their ground echelon is trapped in Bataan.
British Government: Prime Minister Winston Churchill continues his government shakeup following the loss of Singapore and the successful German Channel Dash. Among new appointees are Lord Wolmer as Minister of Economic Warfare and Sir James Grigg as Secretary of War. Everyone knows that Churchill, working very hard every day, is making all the big decisions and that his war cabinet basically exists to rubberstamp them.
American Homefront: While the major auto manufacturers closed down their production lines by 10 February, a few have continued producing cars past that date. That production ends today. The remaining manufacturers all end their production of automobiles on February 22, 1942. Units manufactured at the beginning of February bring up the total number of vehicles in a newly established car stockpile to 520,000. These are available for the duration of the war for rationed sales by auto dealers to purchasers deemed “essential drivers.” Naturally, this makes obtaining a "new" car exceedingly difficult and reliant on "knowing the right people" and "pulling strings." Even if you have a car, gasoline to use it also is rationed.
"A String of Pearls" by Glenn Miller and His Orchestra is the number one song on the Billboard singles chart. It spends ten weeks there.
US Navy submarine USS Swordfish disembarks Philippine President Manuel Quezon and his party at San Jose, Panay. Quezon wants to set up a new headquarters in Mindanao, but the Allies want him out of the Philippines and in Australia. They fear that Quezon may make a separate peace with the Japanese, which would remove from battle many troops fighting hard in the Bataan Peninsula. Area commander General Douglas MacArthur, meanwhile, also has orders to leave the Philippines and head to Australia.
After dark, two flights of 3 B-17Es of the Kangaroo Squadron (435th Bomb Squadron of the 19th Bomb Group), six bombers in all, set out from Townsville (Queensland) Field to bomb the Japanese fortress at Rabaul. The raid will actually take place early on the morning of the 23rd. One of these B-17s is "Swamp Ghost," which later becomes famous for being found in the swamps of New Guinea. The area has become too hot now for the US Navy to realize its plans of sending a carrier task force to attack the port, which rapidly is becoming the main Japanese base in the southwest Pacific.
European Air Operations: After dark, RAF Bomber Command sends 50 bombers (31 Wellingtons and 19 Hampdens) to attack Wilhelmshaven. The targets are German heavy cruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau ("Salmon and Gluckstein" as the British call them, after the tobacconist), which are believed to be at anchor. The weather is poor for bombing and bombers attempt to release their loads over the city instead (and, according to the Germans, they all miss Wilhelmshaven entirely). Seven bombers attack Emden, five bombers bomb the port of Ostend, five Manchesters lay mines off of Wilhelmshaven, and two Hampdens drop leaflets over Paris. The RAF loses no aircraft.
 |
| The Lone Ranger comic strip by Charles Flanders, illustrator. Taken from The Shreveport Times. February 22, 1942. |
U-96 (Kptlt. Heinrich Lehmann-Willenbrock), on its third patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes and sinks 6,999-ton British freighter Scottish Standard, a straggler from Convoy ONS-67 The crew of Scottish Standard already has abandoned the ship after bombing by a German Focke-Wulf Fw200 Condor, but Lehmann-Willenbrock gladly administers the coup de grâce at 15:52. There are five dead and 39 survivors.
U-96 also hits 8888-ton British tanker Kars, another straggler, this one from Convoy HX-175 (convoys often overlap on the busy North Atlantic routes). The ship is abandoned and taken in tow. Kars makes it to Halifax and is beached on 27 February. There are 50 deaths and two survivors.
 |
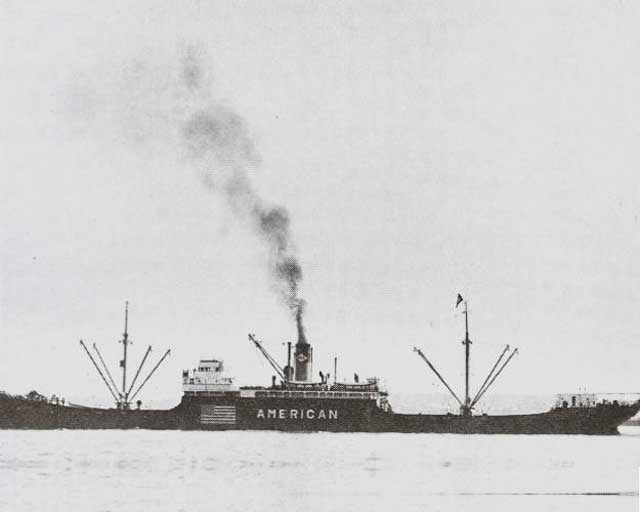
| MV Adellen, sunk on 22 February 1942 by U-155. |
U-128 (Kptlt. Ulrich Heyse), on its second patrol out of Lorient, torpedoes and sinks unescorted 8103-ton US tanker Cities Service Empire about 25 miles north of Bethel Shoals, Florida. Heyse fires four torpedoes at the ship but misses with all four. He then fires two more torpedoes. These hit and immediately start a raging fire. There are 14 dead and 36 survivors.
 |
| British supply ship Hanne, sunk by Luftwaffe bombers off North Africa on 22 February 1942. |
U-83 (Kptlt. Hans-Werner Kraus), on its fifth patrol out of Salamis, claims to hit two ships near Sidi Barrani with torpedoes. This may be true, but there are no records of damaged ships at this time and place.
 |
| The 22 February 1942 L.A. Japanese Daily News reports on "Hundreds taken in round-up" by the FBI. |
Holocaust: German Einsatzgruppe C sets up the Dzyatlava Ghetto (Zdzięcioł Ghetto) in Western Belarus when troops plaster city walls with posters directing the 4500 Jewish residents to relocate to an area around the synagogue and the Talmud Torah building within the streets of Łysogórska and Słonimska. Other residents are forced to evacuate their homes (which they gladly do so as to not be in the Ghetto themselves) and they are used for the new arrivals. The Ghetto is at least partially surrounded by barriers and barbed wire, with guards controlling access. Some trade is permitted between residents of the Ghetto and people outside for things like food and clothing, but these interactions are extremely limited. The Ghetto residents are used for building tasks outside the Ghetto under close guard.
 |
| The Seattle Sunday Times reports on FBI roundups of "Axis Spy Groups," 22 February 1942. |
 |
| Air Marshal Arthur "Bomber" Harris at his office during World War 2. |
The German people entered this war under the rather childish delusion they were going to bomb everyone else, and nobody was going to bomb them. At Rotterdam, London, Warsaw and half a hundred other places, they put their rather naive theory into operation. They sowed the wind, and now, they are going to reap the whirlwind.There is no question that Harris' strategy is effective at destroying cities, though the scope of its effect on the overall German war effort is debatable. The strategy fails utterly at undermining the Reich's morale, just as Hermann Goering's terror bombing of London failed in 1940 and 1941. Bomber Harris becomes a controversial figure within Britain and elsewhere both during and after the war due to his uncompromising and unwavering attitude toward bombing civilians.
 |
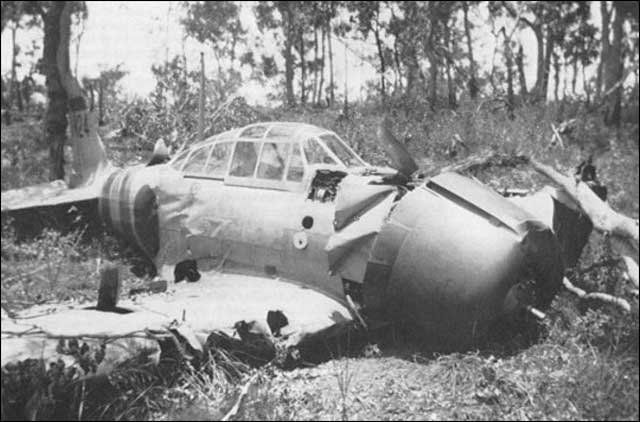
| "Army's new dive bombers see action at Bali," says the caption to this photo in the 22 February 1942 Philadelphia Inquirer. |
US Navy seaplane tender USS Langley leads a convoy of ships out of Freemantle, Australia, to India and Tjilatjap, Java. They carry 69 USAAF P-40s, motor vehicles, and U.S. Army troops
The A-24s of the 17th Bombardment Squadron, 27th Bomber Group, arrive at Batchelor from Brisbane, Australia. As with many air units in the region, their ground echelon is trapped in Bataan.
British Government: Prime Minister Winston Churchill continues his government shakeup following the loss of Singapore and the successful German Channel Dash. Among new appointees are Lord Wolmer as Minister of Economic Warfare and Sir James Grigg as Secretary of War. Everyone knows that Churchill, working very hard every day, is making all the big decisions and that his war cabinet basically exists to rubberstamp them.
 |
| "Corporate Cat," a Gold Seal Novel by Martin Flavin, reprint included with the 22 February 1942 Philadelphia Inquirer. Illustrator: Henry C. Pitz. |
"A String of Pearls" by Glenn Miller and His Orchestra is the number one song on the Billboard singles chart. It spends ten weeks there.
Future History: Christine Margaret Keeler is born in Uxbridge, Middlesex, England. She becomes a waitress, then a topless showgirl, in the late 1950s. Through this work, Keeler meets osteopath Stephen Ward, who introduces her to various government and entertainment figures. Keeler has affairs with several prominent men, including Secretary of State for War John Profumo and Soviet officer Yevgeny Ivanov. This leads to a major British government scandal that results in the resignation of Profumo and the suicide of Ward. After the Profumo Scandal, Keeler slips back into anonymity and passes away in obscurity on 4 December 2017.
February 1942
February 1, 1942: The US Navy Strikes Back
February 2, 1942: Germans Recovering in Russia
February 3, 1942: Japanese Shell and Bomb Singapore
February 4, 1942: Battle of Makassar Strait
February 5, 1942: Empress of Asia Sunk
February 6, 1942: The Christmas Island Body
February 7, 1942: The Double-V Campaign
February 8, 1942: Japan Invades Singapore
February 9, 1942: French Liner Normandie Capsizes
February 10, 1942: US Car Production Ends
February 11, 1942: Tomforce Fails on Singapore
February 12, 1942: The Channel Dash
February 13, 1942: Japanese Paratroopers In Action
February 14, 1942: RAF Orders Terror Raids
February 15, 1942: Japan Takes Singapore
February 17, 1942: Indian Troops Defect to Japanese
February 18, 1942: Battle of Badung Strait
February 19, 1942: FDR Authorizes Internment Camps
February 20, 1942: O'Hare the Hero
February 21, 1942: Crisis in Burma
February 22, 1942: Bomber Harris Takes Over
February 23, 1942: Bombardment of Ellwood, California
February 24, 1942: US Raid on Wake Island
February 25, 1942: Battle of Los Angeles
February 26, 1942: Gneisenau Eliminated
February 27, 1942: Battle of Java Sea
February 28, 1942: Battle of Sunda Strait
2020