Saturday 19 October 1940
 |
| Kapitänleutnant Günther Prien has a terrific 48 hours as he participates in the attacks on Convoy HX 79 on 19 October 1940 (Schulte, Federal Archive). |
Overview: With the Battle of Britain winding down on 19 October 1940, the real action is moving out to sea. The period 18-20 October 1940 is one of the most devastating of the war for the British due to huge losses at sea. Air raids can be handled, though of course they inflict great punishment; but Britain relies on imports for its very survival. Winston Churchill later comments that the war at sea was always his greatest concern during the war's early years, and, as discussed below, today is an extreme example of why that is.
Battle of Britain: The poor weather continues, restricting flight operations. There are scattered reconnaissance flights and an occasional "pirate raid," with some houses destroyed in Coventry.
At 14:00, some fighter-bombers (Jabos) set out for London, but they don't accomplish anything. At 15:00, the day's major daylight raid takes place. About 60 aircraft, including some Dornier Do 17s and Junkers Ju 88s, head for London. The RAF sends up five squadrons to intercept them. The RAF loses a couple of Spitfires.
The poor weather continues into the night, but the Luftwaffe attacks the usual targets: London, Liverpool, Manchester, Coventry, Birmingham, Bristol, and South Wales. London takes the brunt of the attack, with the rail lines and dockyards suffering greatly. In the silver lining department, so much has been destroyed in the dockyards area that the bombs only stir up old debris. Eastbourne also takes damage to its gas works, where the gasometer is damaged.
Overall, it is a quiet day and a rare "victory" for the Luftwaffe. It loses two planes to the RAF's five. The Luftwaffe tends to do well on days with little action, whereas it gets its head handed to it when it mounts massive daylight attacks.
Pips Priller, 6./JG 51, gets his 20th victory and is awarded the Knight's Cross (Ritterkreuz). Pips Priller is known for a flamboyant lifestyle, driving a fancy red car, and dressing well.
European Air Operations: The weather remains poor today. RAF Bomber Command carries out only a few operations on airfields in northwest Europe and railway installations at Osnabruck.
Battle of the Atlantic: Convoys SC 7 and HX 79 begin to merge in the Western Approaches to Liverpool. A U-boat wolfpack has been attacking SC 7 on the night of 18/19 October, and the convoy's survivors begin to recede to the east. Today, an entirely new convoy, HX 79, hoves into view from the west. The wolfpack begins stalking Convoy HX 79 as well. Yesterday we summarized the attacks on SC 7, which continue through the morning of the 19th; today, we summarize the attacks on HX 79.
Convoy HX 79 is composed of 49 ships that sailed out of Halifax on 8 October. It is about four days from landfall at Liverpool. It had been several days behind Convoy SC 7 but has since almost caught up to it. While originally the convoy had no escorts in the mid-Atlantic, the Admiralty, realizing by reports from Convoy SC 7 that U-boats are in the area, quickly sends 11 Royal Navy vessels (LCdr. Russell) out to protect it. These consist of:
The U-boats wait throughout the day as Convoy HX 79 approaches from the west. As darkness falls, they approach on the surface. Prien brazenly sails into the middle of the convoy from the south, Endrass from the north. This is Prien's favorite tactic, and Endrass had been Prien's second before receiving his current command, so they know what the other is likely to do without communicating. The convoy escort is completely ineffective, as was the one for Convoy SC 7.
After the U-boats are in position, all blazes break loose. The battle continues past midnight into the 20th, but we will look at the entire night's results here.
U-47 sinks (damages) the following ships:
It is a classic U-boat attack. Just like on the previous night, there are burning ships, sinking ships, derelicts getting in the way, lifeboats, U-boats, flotsam, jetsam, explosions, men drowning left and right, ships careening at full speed into the night - everything. The U-boats make a clean getaway, though an armed merchant ship takes a few potshots at U-1010 and misses.
The British take losses elsewhere, too.
Royal Navy destroyer HMS Venetia (Lt Cdr D. L. C. Craig), on a patrol with two other destroyers in the Straits of Dover, hits a mine and sinks off Margate, Kent. There are 34 deaths and 18 other casualties.
Royal Navy 290 ton trawler HMS Velia hits a mine and sinks off the Kentish Knock Lightship. Everyone survives.
British coaster Aridity hits a mine and sinks in the Thames Estuary.
There is a violent storm in eastern Canada. Canadian 221 ton auxiliary minesweeper Bras D'Or sinks in the Gulf of St. Lawrence as a result while engaged in traveling with Romanian freighter (Ingner N. Vlasspol) from Quebec to Sydney, Nova Scotia. There are no survivors among the 29 crew.
Polish submarine Wilk attacks Danish freighter Norge in Lister Fjord but misses.
Convoys OB 231 and OL 8 depart from Liverpool, Convoys FN 312 and FN 314 depart from Southend, Convoy FS 314 departs from Methil.
Battle of the Mediterranean: On the 18th, the Royal Navy obtained documents from Italian submarine Durbo before sinking it. Today, the Royal Navy uses that information to hunt for Italian submarine Lafole operating off Cape Tresforcas.
Royal Navy cruiser HMS Ajax is in port at Alexandria getting repairs for shell holes suffered in its encounter with Italian destroyers on 12 October.
Brazilian 8265 ton freighter Ipanemaloide (formerly the Cuma) sinks in the Mediterranean south of Sicily. This is usually ascribed to a torpedo hit, but there are numerous minefields in the area and that may have been the cause.
The RAF attacks Italian positions at Benghazi, Berka, Halfaya, Maritza (in the Dodecanese), and Diredawa, Abyssinia. The Italians respond during the night with attacks on Cairo, Bahrain, and Saudi Arabia, targeting British ARAMCO oil installations. There are reports in the press that the Italians are sending out patrols in anticipation of a continuation of their offensive, but the Italian Commando Supremo has its eyes on Greece, not North Africa.
At Malta, Governor Dobbie once again complains about the mail and newspaper service to the island. Everything comes around Africa and takes weeks, if not months, to reach soldiers stationed on Malta. This is creating a real morale problem. For instance, at this time, the latest mail received by the troops is from August, and some just recently received is from as far back as May. This was before the start of the bombing of London, so there is increasing anxiety about the safety of relatives and property.
General Sir Alan Cunningham becomes commander of British forces in East Africa.
Italian/German Relations: While the Germans are frantically trying to uncover Italian intentions toward Greece using their own sources, Italian Foreign Minister Count Ciano continues to dribble out information. Today, he sends a telegram summarizing the planned invasion but puts the start date as 23 October. In fact, the projected start date is 28 October, as he should know. Shortly after, German Ambassador to Rome Hans Georg Mackensen telegrams that Ciano has informed him that Hitler has approved Mussolini's plan to attack Greece. This is news to Ribbentrop, who was present at the Brenner Pass meeting and has no inkling that this was supposedly discussed. Upon being informed of these communications, Hitler tells Ribbentrop to do nothing regarding the matter - which some interpret as approval of the invasion by silence. However, the entire affair is muddled and subject to interpretation.
Spanish/German Relations: The OKW completes planning for Operation Felix. This, however, requires the participation of Spain, and thus Spanish entry into the war.
Reichsfuhrer-SS Heinrich Himmler travels by train to Spain to meet with Franco and get in a little tourist time devoted to his mystical beliefs about German ancestors.
German Government: Hitler decides to meet with French leader Petain and Spanish leader Franco. He will depart on his train Amerika late on the 20th.
US Military: The US Army Air Corps establishes the Hawaiian Air Force at Fort Shafter.
Light cruiser USS St. Louis departs from Guantanamo Bay Naval Station for San Juan, Puerto Rico. It is carrying the Greenslade Board to examine British bases received in the destroyers-for-bases deal.
Soviet Military: The Stavka plans a major ship-building program.
Spain: Belgian Prime Minister Pierlot and Foreign Minister Spaak have been interned in Barcelona since the fall of Belgium in May. They elude their captors and escape to neutral Portugal hidden in a truck. Technically they can also be interned there, too, but the Portuguese government is notorious for not doing so.
Australia: A convoy, US 6, carrying the Australian 7th Division, Australian Imperial Air Force, 20th Infantry Brigade and 21st Infantry Brigade sets sail for the Middle East.
Future History: Michael Gambon is born in Cabra, Dublin. He becomes a British television actor, later a famous Hollywood actor, and throughout a respected stage actor. He remains active, though he has retired from the stage.
October 1940
October 2, 1940: Hitler's Polish Plans
October 3, 1940: British Cabinet Shakeup
October 4, 1940: Brenner Pass Meeting
October 5, 1940: Mussolini Alters Strategy
October 6, 1940: Iron Guard Marches
October 7, 1940: McCollum Memo
October 8, 1940: Germans in Romania
October 9, 1940: John Lennon Arrives
October 10, 1940: Führer-Sofortprogramm
October 11, 1940: E-Boats Attack!
October 12, 1940: Sealion Cancelled
October 13, 1940: New World Order
October 14, 1940: Balham Tragedy
October 15, 1940: Mussolini Targets Greece
October 16, 1940: Japanese Seek Oil
October 17, 1940: RAF Shakeup
October 18, 1940: Convoy SC-7 Catastrophe
October 19, 1940: Convoy HX-79 Catastrophe
October 20, 1940: Convoy OB-229 Disaster
October 21, 1940: This Evil Man Hitler
October 22, 1940: Aktion Wagner-Burckel
October 23, 1940: Hitler at Hendaye
October 24, 1940: Hitler and Petain
October 25, 1940: Petain Woos Churchill
October 26, 1940: Empress of Britain Attack
October 27, 1940: Greece Rejects Italian Demands
October 28, 1940: Oxi Day
October 29, 1940: US Draft Begins
October 30, 1940: RAF Area Bombing Authorized
October 31, 1940: End of Battle of Britain
2020
Battle of Britain: The poor weather continues, restricting flight operations. There are scattered reconnaissance flights and an occasional "pirate raid," with some houses destroyed in Coventry.
At 14:00, some fighter-bombers (Jabos) set out for London, but they don't accomplish anything. At 15:00, the day's major daylight raid takes place. About 60 aircraft, including some Dornier Do 17s and Junkers Ju 88s, head for London. The RAF sends up five squadrons to intercept them. The RAF loses a couple of Spitfires.
The poor weather continues into the night, but the Luftwaffe attacks the usual targets: London, Liverpool, Manchester, Coventry, Birmingham, Bristol, and South Wales. London takes the brunt of the attack, with the rail lines and dockyards suffering greatly. In the silver lining department, so much has been destroyed in the dockyards area that the bombs only stir up old debris. Eastbourne also takes damage to its gas works, where the gasometer is damaged.
Overall, it is a quiet day and a rare "victory" for the Luftwaffe. It loses two planes to the RAF's five. The Luftwaffe tends to do well on days with little action, whereas it gets its head handed to it when it mounts massive daylight attacks.
Pips Priller, 6./JG 51, gets his 20th victory and is awarded the Knight's Cross (Ritterkreuz). Pips Priller is known for a flamboyant lifestyle, driving a fancy red car, and dressing well.
European Air Operations: The weather remains poor today. RAF Bomber Command carries out only a few operations on airfields in northwest Europe and railway installations at Osnabruck.
 |
| U-100 on the final approach to the German base at Lorient. |
Convoy HX 79 is composed of 49 ships that sailed out of Halifax on 8 October. It is about four days from landfall at Liverpool. It had been several days behind Convoy SC 7 but has since almost caught up to it. While originally the convoy had no escorts in the mid-Atlantic, the Admiralty, realizing by reports from Convoy SC 7 that U-boats are in the area, quickly sends 11 Royal Navy vessels (LCdr. Russell) out to protect it. These consist of:
- Destroyers HMS Whitehall and HMS Sturdy
- Corvettes HMS Hibiscus, HMS Heliotrope, HMS Coreopsis, and HMS Arabis
- A/S Trawlers HMS Lady Elsa, HMS
- Blackfly, HMS Angle
- Minesweeper HMS Jason
- Submarine O-14
U-47 (Kapitänleutnant Günther Prien);Everything is being coordinated and controlled by Konteradmiral Karl Dönitz at his U-boat headquarters in Lorient. Doenitz relays instructions through Prien, who spotted the convoy originally. The sequential attacks on Convoy SC 7 and HX 79 are the first classic wolfpack action of the war, though there has been some small-scale cooperation previously.
U-100 (Joachim Schepke);
U-46 (Engelbert Endrass);
U-48 (Heinrich Bleichrodt); and
U-38 (Heinrich Liebe).
The U-boats wait throughout the day as Convoy HX 79 approaches from the west. As darkness falls, they approach on the surface. Prien brazenly sails into the middle of the convoy from the south, Endrass from the north. This is Prien's favorite tactic, and Endrass had been Prien's second before receiving his current command, so they know what the other is likely to do without communicating. The convoy escort is completely ineffective, as was the one for Convoy SC 7.
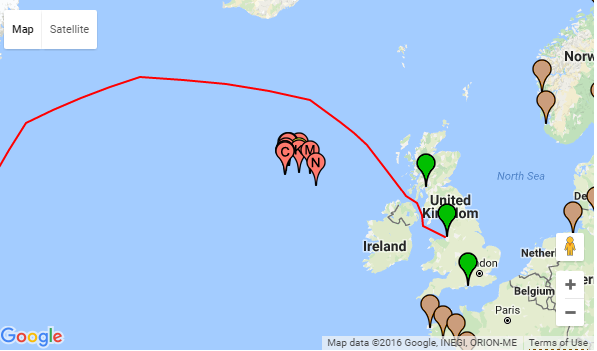 |
| Location of the attack on Convoy HX 79. |
U-47 sinks (damages) the following ships:
- 4966-ton Uganda
- 6023-ton Shirak (damaged)
- 4947-ton Wandby
- 5185-ton La Estancia
- 5026-ton Whitford Point
- 8995-ton Athelmonarch (damaged).
- 8230-ton Caprella
- 6218-ton Sitala
- 5452-ton Loch Lomond
- 4548- ton Ruperra
- 9965-ton Janus
- 7653-ton Matheran
- 6856-ton Bilderdijk
- 6023-ton Shirak (U-47 damages her first)
It is a classic U-boat attack. Just like on the previous night, there are burning ships, sinking ships, derelicts getting in the way, lifeboats, U-boats, flotsam, jetsam, explosions, men drowning left and right, ships careening at full speed into the night - everything. The U-boats make a clean getaway, though an armed merchant ship takes a few potshots at U-1010 and misses.
The British take losses elsewhere, too.
Royal Navy destroyer HMS Venetia (Lt Cdr D. L. C. Craig), on a patrol with two other destroyers in the Straits of Dover, hits a mine and sinks off Margate, Kent. There are 34 deaths and 18 other casualties.
Royal Navy 290 ton trawler HMS Velia hits a mine and sinks off the Kentish Knock Lightship. Everyone survives.
British coaster Aridity hits a mine and sinks in the Thames Estuary.
There is a violent storm in eastern Canada. Canadian 221 ton auxiliary minesweeper Bras D'Or sinks in the Gulf of St. Lawrence as a result while engaged in traveling with Romanian freighter (Ingner N. Vlasspol) from Quebec to Sydney, Nova Scotia. There are no survivors among the 29 crew.
Polish submarine Wilk attacks Danish freighter Norge in Lister Fjord but misses.
Convoys OB 231 and OL 8 depart from Liverpool, Convoys FN 312 and FN 314 depart from Southend, Convoy FS 314 departs from Methil.
 |
| Winnipeg Ukrainians (note native dress) gather to promote a concert they are giving on the 23rd to raise money for the war effort. Among the performers: radio artists The Dirty Dozen. Winnipeg Free Press Archives. |
Royal Navy cruiser HMS Ajax is in port at Alexandria getting repairs for shell holes suffered in its encounter with Italian destroyers on 12 October.
Brazilian 8265 ton freighter Ipanemaloide (formerly the Cuma) sinks in the Mediterranean south of Sicily. This is usually ascribed to a torpedo hit, but there are numerous minefields in the area and that may have been the cause.
The RAF attacks Italian positions at Benghazi, Berka, Halfaya, Maritza (in the Dodecanese), and Diredawa, Abyssinia. The Italians respond during the night with attacks on Cairo, Bahrain, and Saudi Arabia, targeting British ARAMCO oil installations. There are reports in the press that the Italians are sending out patrols in anticipation of a continuation of their offensive, but the Italian Commando Supremo has its eyes on Greece, not North Africa.
At Malta, Governor Dobbie once again complains about the mail and newspaper service to the island. Everything comes around Africa and takes weeks, if not months, to reach soldiers stationed on Malta. This is creating a real morale problem. For instance, at this time, the latest mail received by the troops is from August, and some just recently received is from as far back as May. This was before the start of the bombing of London, so there is increasing anxiety about the safety of relatives and property.
General Sir Alan Cunningham becomes commander of British forces in East Africa.
 |
| Military men have very practical reasons for wanting to get news from home. Saturday Evening Post, 19 October 1940. |
Spanish/German Relations: The OKW completes planning for Operation Felix. This, however, requires the participation of Spain, and thus Spanish entry into the war.
Reichsfuhrer-SS Heinrich Himmler travels by train to Spain to meet with Franco and get in a little tourist time devoted to his mystical beliefs about German ancestors.
German Government: Hitler decides to meet with French leader Petain and Spanish leader Franco. He will depart on his train Amerika late on the 20th.
 |
| Actress Anne Nagel shows how to celebrate the upcoming US holiday of Halloween, 1940. |
Light cruiser USS St. Louis departs from Guantanamo Bay Naval Station for San Juan, Puerto Rico. It is carrying the Greenslade Board to examine British bases received in the destroyers-for-bases deal.
Soviet Military: The Stavka plans a major ship-building program.
Spain: Belgian Prime Minister Pierlot and Foreign Minister Spaak have been interned in Barcelona since the fall of Belgium in May. They elude their captors and escape to neutral Portugal hidden in a truck. Technically they can also be interned there, too, but the Portuguese government is notorious for not doing so.
Australia: A convoy, US 6, carrying the Australian 7th Division, Australian Imperial Air Force, 20th Infantry Brigade and 21st Infantry Brigade sets sail for the Middle East.
Future History: Michael Gambon is born in Cabra, Dublin. He becomes a British television actor, later a famous Hollywood actor, and throughout a respected stage actor. He remains active, though he has retired from the stage.
 |
| Early snow in Delaware, USA signals the change of seasons. |
October 1940
October 2, 1940: Hitler's Polish Plans
October 3, 1940: British Cabinet Shakeup
October 4, 1940: Brenner Pass Meeting
October 5, 1940: Mussolini Alters Strategy
October 6, 1940: Iron Guard Marches
October 7, 1940: McCollum Memo
October 8, 1940: Germans in Romania
October 9, 1940: John Lennon Arrives
October 10, 1940: Führer-Sofortprogramm
October 11, 1940: E-Boats Attack!
October 12, 1940: Sealion Cancelled
October 13, 1940: New World Order
October 14, 1940: Balham Tragedy
October 15, 1940: Mussolini Targets Greece
October 16, 1940: Japanese Seek Oil
October 17, 1940: RAF Shakeup
October 18, 1940: Convoy SC-7 Catastrophe
October 19, 1940: Convoy HX-79 Catastrophe
October 20, 1940: Convoy OB-229 Disaster
October 21, 1940: This Evil Man Hitler
October 22, 1940: Aktion Wagner-Burckel
October 23, 1940: Hitler at Hendaye
October 24, 1940: Hitler and Petain
October 25, 1940: Petain Woos Churchill
October 26, 1940: Empress of Britain Attack
October 27, 1940: Greece Rejects Italian Demands
October 28, 1940: Oxi Day
October 29, 1940: US Draft Begins
October 30, 1940: RAF Area Bombing Authorized
October 31, 1940: End of Battle of Britain
2020
No comments:
Post a Comment