Tuesday 27 May 1941
 |
| "HMS RODNEY with BISMARCK covered by smoke in the distance, 27 May 1941." © IWM (MH 15929). |
The German military mission also is under intense pressure in Iraq. The Luftwaffe force has been vastly reduced in size, while the eleven Italian Fiat Cr-42 fighters that have just arrived can do little. All continue to fight, but prepare to leave the country should Baghdad fall.
As the British near Baghdad, rioting and looting begin to break out.
In London, Prime Minister Winston Churchill tells the House that "In Iraq, our position has been largely re-established, and the prospects have greatly improved."
European Air Operations: RAF Bomber Command sends 14 aircraft on anti-shipping sweeps during the day. It attacks Cologne during the night with 84 aircraft and also lays mines off Boulogne, Brest and St. Nazaire.
The Luftwaffe performs an armed reconnaissance across the Channel. The Germans lose a Heinkel He 111 from 4./KG 55 west of St. Ives, Cornwall to Pilot/Officer F. Oliver of RAF No 66 Squadron.
 |
| German battleship Bismarck under fire from battleships HMS Rodney and King George V (photo from the collection of P.O. George H. J. Monk, R.N., courtesy of Reg Monk). |
Everyone on the Bismarck knows the situation is hopeless. Around midnight, Admiral Günther Lütjens, in command aboard the Bismarck, makes his last radio transmission to headquarters: "Ship unmaneuverable. We shall fight to the last shell. Long live the Führer."
The Royal Navy's 4th Destroyer Flotilla, under the command of Captain Philip Vian, arrives on the scene after being diverted from escorting troop convoy WS8B from Glasgow to the Indian Ocean. His destroyers make runs at the battleship, launching torpedoes. It is unclear (and unlikely) if the destroyers make any hits, but they keep the Germans busy.
U-556 (Kptlt. Herbert Wohlfarth), which has completed its patrol with Wolfpack West in the North Atlantic and returning to base in France, receives orders to retrieve the logbooks from Bismarck. Wohlfarth heads to the position, and on his way spots aircraft carrier Ark Royal and the battlecruiser Renown. However, U-556 is out of torpedoes and can do nothing.
 |
| Bismarck under fire from the Royal Navy, 27 May 1941 (photo from the collection of P.O. George H. J. Monk, R.N., courtesy of Reg Monk). |
Heavy cruiser Dorsetshire then closes and sends three torpedoes into the blazing German ship. Around the same time, the surviving Bismarck crew sets off scuttling charges. It is unclear if the torpedoes would have sunk the Bismarck, or if it required the Bismarck crew scuttling the now-defenseless ship - but the Bismarck capsizes and sinks at 10:40.
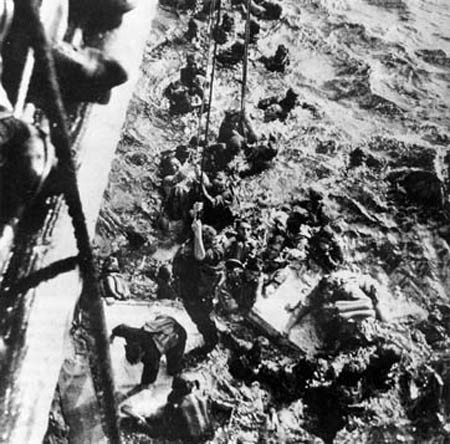 |
| Survivors of the Bismarck being pulled aboard HMS Dorsetshire. |
Operation Rheinübung involved two ships: Bismarck and heavy cruiser Prinz Eugen. The latter ship is forgotten by virtually everyone, Prinz Eugen - almost out of fuel - has made a rendezvous with tanker Spichern far to the south. Today, it develops some engine trouble, reducing its speed to 28 knots. Ultimately, this will force Prinz Eugen to abandon its mission and seek haven in France.
At Berchtesgaden, Hitler crony Walther Hewel notes in his diary, "Bismarck sunk … Fuehrer melancholy beyond words."
U-107 (Kptlt. Günther Hessler), operating off Freetown, is on its second patrol. It uses two torpedoes to sink 5108-ton British freighter Colonial, which has been dispersed from Convoy OB 318. 100 men, including Convoy Commodore Rear Admiral W.B. Mackenzie RN, are picked up by target ship (formerly battleship) HMS Centurion and landed at Freetown.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 239 Royal Navy ton minesweeping trawler Evesham off Yarmouth. Everyone survives.
The Luftwaffe damages anti-aircraft ship HMS Alynbank off Cape Cornwall. There are 65 deaths.
The Luftwaffe bombs and damages ocean boarding vessel HMS Registan in Bristol Channel. The master beaches it at Falmouth, Cornwall, and the Registan is later refloated and repaired. There are 70 deaths. Those lost include Dudley Joel, 37, a British businessman and a Member of Parliament. Some sources place this as happening on the 28th.
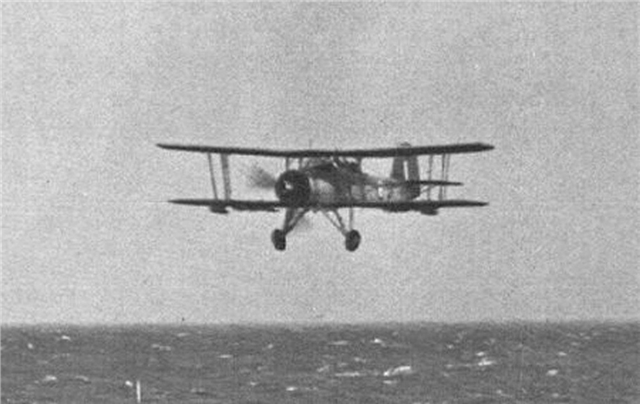 |
| Swordfish 5S of 818 Squadron, FAA returns to HMS Ark Royal after observing the sinking of Bismarck. |
Norwegian 1655-ton freighter Thyra, part of Convoy OB 325, collides with escort destroyer HMS Leamington and sinks. There are four deaths, and 20 survivors are taken aboard the Leamington, which is largely unscathed.
British 7628-ton freighter Michael E has been converted into the first Royal Navy Catapult Aircraft Merchant (CAM) ship. It sails late in the day from Glasgow for Halifax, Nova Scotia with Convoy OB 327 on its first mission carrying a Hawker Hurricanes modified for sea duty.
Minelayer Teviotbank lays minefield BS.62 in the English Channel.
Convoy OB 327 departs from Liverpool. Convoy HX 129, delayed by the Bismarck battle, departs from Halifax and BHX departs from Bermuda. Convoy HX 129, incidentally, becomes the first convoy to have continuous escort protection across the Atlantic due to the new escort headquarters at St. John's.
 |
| "A Fairey Swordfish flying over HMS KING GEORGE V during the BISMARCK action." © IWM (MH 15930) (photo from the collection of P.O. George H. J. Monk, R.N., courtesy of Reg Monk). |
After an hour or two of the unequal battle, British commander Lieutenant-General William "Strafer" Gott authorizes a withdrawal. Lieutenant-Colonel J. Moubray, in command of the 3rd Battalion Coldstream Guards and the other units garrisoning the pass (including the 4th Royal Tank Regiment (4th RTR, Major C. G. Miles), field, anti-tank and anti-aircraft guns, and the 7th Support Group of the 7th Armoured Division), blasts his way out of his encirclement with some troops captured by Group Bach.
While not a major battle, Operation Skorpion deprives the British of their last gain from their Operation Brevity of May 15-16. It also provides an unusual incident where the roles of the two sides are reversed, the Germans being able to intercept some British wireless messages while the British get no help from Ultra. The British Army loses 173 men (40 prisoners), four 25-pounder field guns, eight 2-pounder anti-tank guns, and five Infantry tanks. The Germans capture nine 25-pounder field guns, seven Matilda (A12) tanks, and two other tanks. Most importantly, the battle eliminates any British hope of a quick relief of Tobruk.
The Afrika Korps wastes no time in reinforcing its defenses both at Tobruk and along the Gazala Line. Rommel orders a defensive line built just over the border in Egypt, based on Halfaya Pass, in an arc through Qalala and Hafid Ridge 6 miles (9.7 km) south-west of Fort Capuzzo to Sidi Aziz.
At 00:50, Churchill sends Wavell a brief cable, "Hope you are preparing your desert stroke and that Tobruk will not be idle." The British in Egypt now brings forward the tanks from the Tiger Convoy (Churchill's "Tiger Cubs") for another offensive planned in mid-June (Operation Battleaxe). At the evening War Cabinet meeting, Admiral Sir Dudley Pound emphasizes the "vital importance from the naval point of view of the recapture of Cyrenaica."
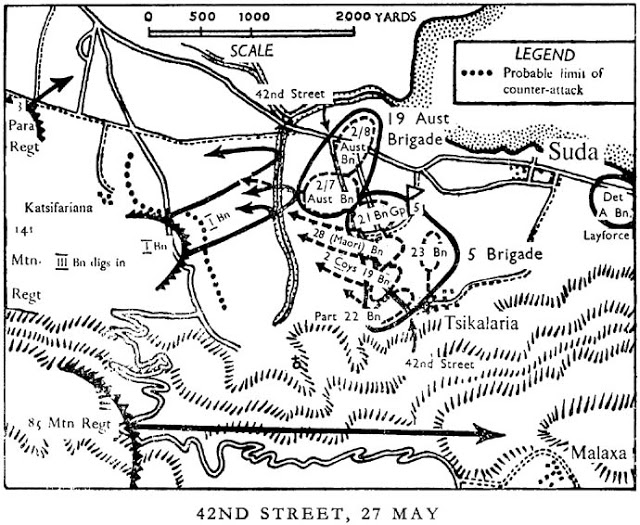 |
| A map of the Battle of 42nd Street, Suda, Crete, 27 May 1941. |
At 02:00, Prime Minister Winston Churchill cables Middle East Commander General Archibald Wavell: "Victory in Crete essential at this turning point in the war. Keep hurling in all aid you can." At 08:42, Wavell responds. He has a much closer view of the actual situation on Crete and knows that events at sea or in Iraq mean nothing for his defense of the island. Wavell cables back, "Fear we must recognize that Crete is no longer tenable…."
Wavell's cable arrives while the War Cabinet is in session. As the meeting's minutes state:
The Prime Minister said that all chances of winning the battle in Crete now appeared to have gone and we should have to face the prospect of the loss of most of our forces there.Churchill casually adds that he will reveal nothing of this to the House of Commons in his morning statement. In fact, he simply states that the army's "magnificent resistance hangs in the balance."
 |
| Fallschirmjäger march into Canea (Chandia/Hania) after a long battle, 27 May 1941 (Australian War Memorial 106492). |
In view of General Wavell's latest message, he should be ordered to evacuate Crete forthwith, saving as many men as possible without regard to material, and taking whatever measures, whether by reinforcement or otherwise, are best.So, London now accepts the inevitable. British island commander General Bernard Freyberg quickly orders Allied troops to begin withdrawing to the south shore for evacuation. The British troops at Suda and Beritania, including 800 Commandos just landed on the 26th, begin heading down the road to Vitsilokoumos, north of Sfakia. The Germans occupy the critical naval base at Suda Bay as the British depart.
Responding to an OKW request made on the 26th, the Italians send a convoy from Rhodes to reinforce the Germans on Crete. It contains a brigade from the 50th Infantry Division Regina, supported by 13 L3/35 light tanks. As many have noted, Operation Mercury has been an odd battle because the Germans have had no tanks, and the British Army has had no air support. This Italian convoy, comprising a motley collection of four fishing vessels, two steamships, one riverboat, two reefer ships, three tugs, and three tankers, aims to bring ashore some Axis armored support. Their planned landing date is the afternoon of 28 May. The convoy is escorted by destroyer Crispi and two torpedo boats (Lince and Lira).
Royal Navy battleship HMS Barham is covering the withdrawal of minelayer Abdiel from Suda Bay, where it landed Commandos on the 26th when the Luftwaffe bombs it. The bomb destroys Y turret and kills seven crewmen while wounding six. Barham makes for Alexandria, then Durban, for repairs, which take until 30 July.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 305-ton armed trawler HMT Thorbryn off Tobruk.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 307-ton Naval whaler Syvern en route to Crete.
The Luftwaffe bombs and sinks 1187 ton Greek freighters Antonios and 5452 ton Julia at Suda Bay, Crete. Everyone survives.
The RAF bombs and damages Italian freighter Marco Foscarini off Tripoli. The master beaches her, and the Foscarini is refloated and scrapped after the war.
More troops are embarked on three destroyers (Hotspur, Imperial, and Kimberley) at Alexandria for transport to Crete when the decision to evacuate to the island is received. The troops are not sent.
Royal Navy submarine HMS Unbeaten suffers damage from grounding at Malta and requires repairs until 4 June.
The RAF force based on Malta loses two Blenheims of RAF No. 82 Squadron while attacking a large Italian supply convoy that reaches Tripoli safely. At Malta, the Luftwaffe drops mines in Grand Harbour.
 |
| Commander-in-Chief of the German Army Field Marshal Walther von Brauchitsch at the Corinthian Canal, Greece 27 May 1941. |
POWs: In the House of Commons, Winston Churchill rejects a request that prisoner Rudolf Hess be tried as a spy or illegal alien.
German/Vichy French Relations: Vichy Vice Premier Admiral François Darlan and German ambassador to France, Otto Abetz sign the Paris Protocols. These Protocols grant the Germans military facilities in Syria, Tunisia, and French West Africa, while the French get a reduction in occupation costs (from 20 to 15 million Reichsmarks a day) and the release of 6800 more French POWs. These are not formally ratified, but provide a framework for French collaboration.
US/Japanese Relations: US Ambassador to Japan Joseph Grew sends a cable to Washington:
A member of the Embassy was told by my ------- colleague that from many quarters, including a Japanese one, he had heard that a surprise mass attack on Pearl Harbor was planned by the Japanese military forces, in case of "trouble" between Japan and the United States; that the attack would involve the use of all the Japanese military facilities. My colleague said that he was prompted to pass this on because it had come to him from many sources, although the plan seemed fantastic.Grew's unnamed friend, of course, is absolutely correct - the Japanese have been planning for an attack on US, British and Dutch interests in the Pacific for some time. The US already has a defensive plan prepared for such possibilities, so the ONI (Office of Naval Intelligence) files the warning without acting on it.
Anglo/US Relations: Winston Churchill cables Roosevelt thanking him for the decision to release half a dozen small aircraft carriers to the Royal Navy. "All this will be most helpful."
Anglo/Irish Relations: At the morning War Cabinet meeting - usually held in the evening, but assembled due to the naval battle occurring at the time involving the Bismarck - Churchill gives his thoughts about conscription in Northern Ireland. Irish leader Eamon De Valera has warned against conscription as having a negative effect on public opinion. Churchill opines that a statement should be issued that states in part:
His Majesty's Government had now come to the conclusion that, although there could be no dispute about our rights, or about the merits, it would be more trouble than it was worth to apply conscription to Northern Ireland.The War Cabinet, of course, agrees with this very grudging concession, as it does with virtually everything that Churchill proposes throughout the war. This is exactly what he tells the House.
British Military: Winston Churchill sends a memo to General Ismay which urges expansion of the British paratrooper force "on the German model" based on its success on Crete. If imitation is the sincerest form of flattery, Churchill is paying the Fallschirmjäger a huge compliment. This is somewhat ironic considering the opposite conclusions about Operation Mercury that the German leadership are drawing at this time.
The War Cabinet's "Tank Parliament" meets, and it agrees that tank production must be greatly expanded.
The War Office issues a secret memo barring Fascists and Communists from serving in the Home Guard. All such members currently serving are to be cashiered forthwith.
 |
| The front page of the Syracuse Herald-Journal, 27 May 1941. |
Albania: The Albanian who recently attempted to assassinate the king of Italy and the prime minister of Albania, Vasil Laçi, 19, is executed.
China: The Japanese North China Front Army defeats the Chinese 1st War Area in the Battle of South Shanxi. This is one of the worst land defeats for the Chinese forces of the entire war and is largely due to refusal of the Communist 8th Route Army to rescue trapped Nationalist (Kuomintang) forces. The Nationalists are wiped out despite having an almost 2:1 advance in troop strength.
British Homefront: Prime Minister Winston Churchill makes a radio broadcast to the nation. He states that Britain is heading into a "long, stern, scowling valley of war, to victory."
American Homefront: In a long, rambling radio address broadcast (fireside chat) from the White House, President Roosevelt proclaims a state of unlimited national emergency. He re-uses his famous phrase from 1933, "the only thing we have to fear is fear itself." Roosevelt lists the things the United States has done to support the British war effort, announces new policies which include a decision to:
actively resist wherever necessary, and with all our resources, every attempt by Hitler to extend his ... domination to the Western Hemisphere.He then casts the confrontation as:
divided between human slavery and human freedom—between pagan brutality and the Christian ideal. We choose human freedom—which is the Christian ideal.There is no mention in the speech of actually declaring war, or how the US actions he lists would relate to the proper role of neutrals. It is as close to a declaration of war, and the obvious significance of the speech is that the United States is going to do everything possible to fight German without actually firing weapons.
 |
| USS St. Augustine off the Boston Navy Yard, Massachusetts, 27 May 1941 (Bureau of Ships Collection in the U.S. National Archives). |
May 1941
May 1, 1941: British Hold Tobruk
May 2, 1941: Anglo-Iraq War
May 3, 1941: Liverpool Hammered
May 4, 1941: Hitler Victory Speech
May 5, 1941: Patriots Day
May 6, 1941: Stalin In Command
May 7, 1941: May Blitz
May 8, 1941: Pinguin Sunk
May 9, 1941: U-110 Captured
May 10, 1941: Hess Flies Into History
May 11, 1941: The Hess Peace Plan
May 12, 1941: Tiger Arrives Safely
May 13, 1941: Keitel's Illegal Order
May 14, 1941: Holocaust in Paris
May 15, 1941: Operation Brevity
May 16, 1941: Blitz Ends
May 17, 1941: Habbaniya Relieved
May 18, 1941: Croatia Partitioned
May 19, 1941: Bismarck at Sea
May 20, 1941: Invasion of Crete
May 21, 1941: Robin Moore Sinking
May 22, 1941: Royal Navy Destruction Off Crete
May 23, 1941: Crete Must Be Won
May 24, 1941: Bismarck Sinks Hood
May 25, 1941: Lütjens' Brilliant Maneuver
May 26, 1941: Bismarck Stopped
May 27, 1941: Bismarck Sunk
May 28, 1941: Crete Lost
May 29, 1941: Royal Navy Mauled Off Crete
May 30, 1941: Sorge Warns, Stalin Ignores
May 31, 1941: British Take Baghdad
2020
No comments:
Post a Comment